Unveiling the Microscopic World: Exploring Tiny Arachnids Related to Ticks
The Enigmatic World of Tiny Arachnids
The world of arachnids extends far beyond the familiar spiders and scorpions. A vast and diverse group, encompassing mites, ticks, and harvestmen, these eight-legged creatures play crucial roles in various ecosystems. While many are easily visible to the naked eye, a fascinating realm of tiny arachnids exists, often overlooked but equally important. This exploration delves into the intriguing world of these miniature arthropods, focusing particularly on those related to ticks, highlighting their biological features, ecological impact, and potential significance in human health.
Understanding the Arachnid Family Tree
To appreciate the diversity of tiny arachnids related to ticks, it’s essential to understand their phylogenetic relationships within the class Arachnida. Ticks belong to the order Ixodida, a group characterized by their parasitic lifestyle and the significant impact they have on both animals and humans. However, several other arachnid orders contain species exhibiting similar characteristics, such as microscopic size, ectoparasitic habits, or specific ecological niches that overlap with ticks.
These related orders include mites (Acari), a tremendously diverse group encompassing an overwhelming variety of forms and lifestyles. Within the mites, numerous families share features with ticks, albeit often exhibiting significant morphological differences. Some parasitic mites, for instance, may share similar feeding mechanisms or host preferences with certain tick species.
Tiny Arachnids: A Closer Look at Morphology and Size
The defining characteristic of the tiny arachnids discussed here is their minute size. Many species are barely visible to the naked eye, measuring just a few millimeters or even less in length. This small size influences their morphology, behavior, and ecology in crucial ways. Their tiny bodies are typically highly specialized, reflecting their specific lifestyles. For example, parasitic species often exhibit adaptations for attaching to hosts, such as strong claws or suckers. Others may possess specialized mouthparts adapted for piercing and sucking fluids from plants or other invertebrates.
The reduced size also impacts their reproductive strategies. Many tiny arachnids have a high reproductive rate, compensating for the increased mortality risk associated with their small size and vulnerability to predators. The miniature size also allows them to exploit specific ecological niches inaccessible to larger arthropods.
Ecological Roles and Importance
Despite their small size, these tiny arachnids play significant roles in various ecosystems. Some species are important decomposers, breaking down organic matter and contributing to nutrient cycling. Others are predators, regulating populations of other invertebrates. The parasitic species, while sometimes detrimental to their hosts, can also contribute to ecosystem stability by controlling host populations.
Many species are vital components of the soil food web, influencing plant growth and soil structure. Their presence can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, highlighting the critical role even seemingly insignificant organisms can play in maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
Medical and Veterinary Significance
While most tiny arachnids pose no direct threat to human health, some species can act as vectors for diseases or cause direct harm through bites or infestations. Certain mites, for instance, can cause allergic reactions in humans, while others can infect the skin or respiratory system. Similarly, some tiny arachnids can be parasites of domestic animals, leading to various health problems.
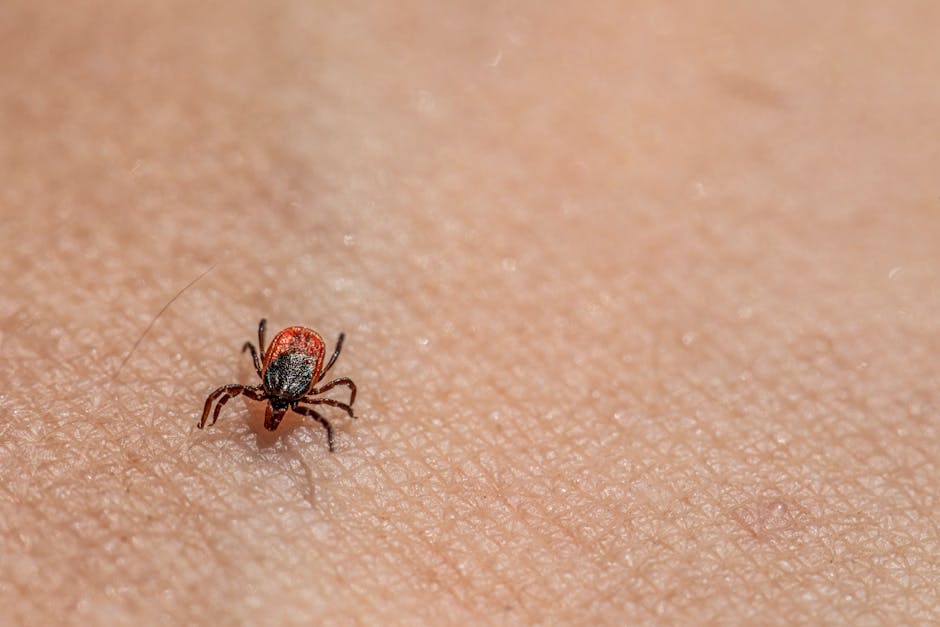

Research into these tiny arachnids and their potential impacts on human and animal health is ongoing. Understanding their biology, ecology, and interactions with other organisms is vital for developing effective strategies for prevention, treatment, and control of related diseases or infestations.
Research Methods and Challenges
Studying tiny arachnids presents unique challenges. Their small size necessitates the use of specialized equipment, such as microscopes and sophisticated sampling techniques. Identifying species often requires detailed microscopic examination, and the subtle morphological variations between species can make accurate identification difficult. Furthermore, the often cryptic behavior and habitat preferences of many species add another layer of complexity to research endeavors.
Advances in molecular techniques, such as DNA barcoding, have significantly aided in the study of these tiny arthropods. These techniques offer the potential to improve species identification and to unravel the evolutionary relationships between species within this complex group.

Conservation Implications
While often overlooked, these tiny arachnids play important ecological roles. Habitat loss and degradation pose serious threats to many species, potentially disrupting ecosystems and affecting their intricate ecological interactions. Conservation efforts focused on preserving biodiversity and maintaining healthy ecosystems are essential for the long-term survival of these often-overlooked creatures.
Future Research Directions
The study of tiny arachnids related to ticks is a rapidly evolving field. Further research into their biology, ecology, and potential roles in disease transmission is vital. This includes exploring new research methodologies, improving species identification, and developing more effective strategies for managing populations of species that have detrimental effects on human or animal health.
Investigation into the genetic diversity and evolutionary history of these arachnids will provide further insight into their adaptations and their ecological roles. Furthermore, understanding their interactions with other organisms, particularly their hosts and predators, is crucial for comprehending their roles within complex ecological networks.
Conclusion: The Unsung Heroes of the Microscopic World
The tiny arachnids related to ticks represent a fascinating and largely unexplored realm of biodiversity. While some species pose risks to human or animal health, many play vital roles in maintaining ecosystem function and stability. Through continued research and conservation efforts, we can gain a deeper appreciation of the crucial role these diminutive creatures play in the intricate web of life.
Further Reading and Resources
This section would list relevant scientific papers, books, and online resources related to arachnids, ticks, and mites. This would enhance the article’s educational value and allow readers to explore the topic further.