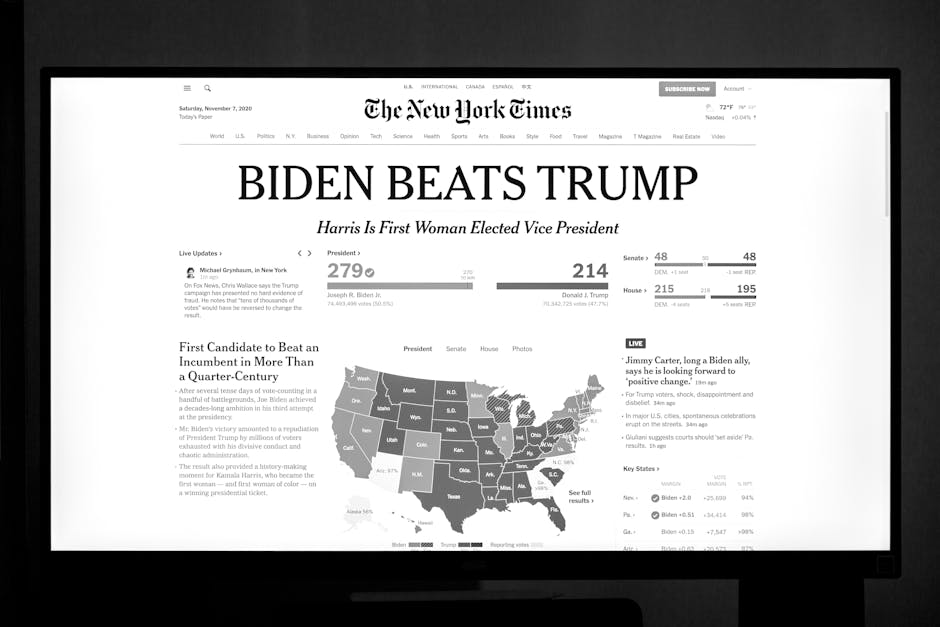
No Tax on Tips Senate Vote: A Deep Dive into the Implications for Workers and the Economy
The Heated Debate Surrounding the No Tax on Tips Senate Vote
The recent Senate vote on eliminating taxes on tips has ignited a firestorm of debate, dividing lawmakers, workers, and economists alike. This complex issue involves intricate legal ramifications, economic consequences, and significant ethical considerations. Understanding the nuances of this legislation requires a comprehensive analysis of its potential impacts, both positive and negative.
Arguments For Eliminating Tip Taxes: A Worker’s Perspective
Proponents of the no tax on tips legislation argue that it would provide much-needed relief to low-wage workers who rely heavily on tips to supplement their income. They contend that current tax laws disproportionately burden these individuals, effectively reducing their already meager earnings. The argument centers on the idea of fairness – that those who work hard and depend on tips should not face unnecessary tax burdens. This perspective highlights the significant financial strain that even small tax deductions can impose on those living paycheck to paycheck. Moreover, advocates claim that removing the tax burden would incentivize better customer service, as workers could retain a larger portion of their earned tips, motivating them to provide exceptional service.
The proponents also argue that the current system of tracking and reporting tip income is often cumbersome and difficult for employees to navigate, leading to errors and potential penalties. Simplifying the tax system for tips would reduce administrative burdens on both workers and the IRS, leading to greater efficiency and improved compliance. The emphasis here is on streamlining the process to make it more user-friendly and less susceptible to errors, thereby benefiting both the worker and the tax agency.
Arguments Against Eliminating Tip Taxes: Economic and Societal Concerns
Opponents of the legislation express concerns about the potential economic consequences of eliminating taxes on tips. They argue that this could lead to a significant reduction in tax revenue, impacting government funding for essential social programs and services. The loss of revenue would need to be compensated for through other means, potentially leading to increased taxes elsewhere or cuts in public spending. This perspective emphasizes the fiscal responsibility of maintaining a stable and sustainable tax system.
Furthermore, critics point to the potential for increased inequality if tips are not taxed. They argue that removing the tax on tips could disproportionately benefit high-earning individuals in industries with high tip potential, widening the gap between higher and lower-income earners. This highlights the importance of considering the broader societal implications of tax policy and its potential effects on income distribution.
Another significant concern is the potential for tax evasion. Without a tax on tips, there’s a greater risk that some workers might underreport their tip income, leading to a loss of revenue for the government and creating an unfair advantage for those who evade taxes. This raises questions about the effectiveness of enforcement mechanisms and the need for robust oversight to prevent widespread non-compliance.

The Senate Vote: A Breakdown of the Process and Outcome
The Senate vote on this crucial legislation was preceded by extensive debates and lobbying efforts from various stakeholders. The process involved various committees scrutinizing the bill, amendments being proposed and debated, and intense negotiations between different political factions. The final vote reflects the complex interplay of political considerations and the competing interests of various constituencies.
Analyzing the voting patterns provides insights into the motivations of individual senators. Understanding the factors that influenced their votes – including their political affiliations, constituency interests, and individual beliefs – helps contextualize the outcome of the vote and its wider implications.
Potential Economic Impacts: A Macroeconomic Perspective
The potential impact of the no-tax-on-tips legislation extends far beyond the individual worker. It has significant macroeconomic implications that require careful consideration. Economists have developed various models to assess the potential impact on employment, inflation, and overall economic growth. These models consider various factors, such as the elasticity of demand for tipped services and the potential for businesses to adjust wages in response to changes in tip income.
Some economists suggest that the removal of tip taxes could lead to a slight increase in employment in the tipped service sector, as businesses might be encouraged to hire more staff. However, this effect could be offset by other factors, such as increased business costs and the potential for reduced consumer spending. The overall net effect on employment remains a subject of ongoing debate among economists.
The Ethical Considerations: Fairness and Equity in Taxation
Beyond the economic considerations, the no tax on tips debate raises important ethical questions about fairness and equity in the tax system. The current tax system already disproportionately affects low-income individuals, and removing the tax on tips could exacerbate this disparity. This prompts a discussion about the moral obligations of the government to ensure a fair and just tax system that does not unduly burden those least able to afford it.
The debate also highlights the complexity of balancing individual needs with the collective good. While removing the tax on tips could directly benefit individual workers, it could potentially harm society as a whole by reducing government revenue needed for vital public services. This ethical dilemma necessitates a thorough examination of societal values and priorities.

International Comparisons: How Other Countries Handle Tip Taxation
Examining how other countries handle tip taxation provides valuable context for the debate. Many countries have different systems for taxing tips, ranging from no tax at all to comprehensive taxation schemes. Analyzing these different approaches allows for a comparative perspective on the potential benefits and drawbacks of each system, informing the ongoing discussion in the U.S.
Comparing different models also sheds light on the challenges and complexities involved in effectively taxing tip income, while considering the unique cultural and economic contexts of each country. This comparative analysis can aid policymakers in designing a more effective and equitable tax system for tipped employees.
Looking Ahead: Future Implications and Potential Reforms
The no tax on tips Senate vote sets the stage for further discussions and potential reforms in the tax system. The outcome of the vote will likely influence future debates surrounding tax policy and the treatment of low-wage workers. Moving forward, policymakers will need to consider various options for reforming the tax system to ensure fairness, efficiency, and sustainability.
Possible reforms could include adjusting the tax brackets for low-income earners, implementing more progressive tax policies, or streamlining the process for reporting and paying taxes on tips. These reforms could aim to alleviate the burden on low-wage workers while also addressing concerns about tax revenue and compliance.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Issue Requiring Careful Consideration
The no tax on tips Senate vote is a complex issue with far-reaching implications for workers, businesses, and the economy as a whole. Understanding the debate requires a nuanced understanding of the economic, ethical, and political factors at play. Moving forward, careful consideration must be given to both the immediate and long-term consequences of any proposed tax policy changes, ensuring that the system is both fair and sustainable.